What Is Spread Betting and How Does It Work?
Spread betting is a popular form of derivative trading that enables you to speculate on the price movements of financial assets, such as indices, forex, commodities, and shares, without owning the underlying asset. Learn everything you need to know about spread betting and understand how it works.
What Is Spread Betting?
Spread betting offers UK traders a way to speculate on financial markets without owning underlying assets. You trade indices, forex, shares and commodities by predicting whether prices will rise or fall. For many UK residents, profits are currently free from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty, which means it is sometimes used as an alternative to traditional share dealing.
However, spread betting is a leveraged product carrying substantial risk. According to data from the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), approximately 80% of retail investor accounts lose money when spread betting and trading CFDs. This guide explains how spread betting works, its potential benefits, the material risks and how to approach it responsibly.
Spread betting is a derivative trading method allowing you to speculate on price movements of financial instruments without purchasing the underlying asset. Instead of buying shares in a company or barrels of oil, you place a bet on whether the price will rise or fall.
The term ’spread’ refers to the difference between the buy price and sell price quoted by your provider. You stake a certain amount per point of price movement. If your prediction is correct, you profit based on how far the price moves favourably. Wrong predictions create losses proportional to adverse movement.
Think of it like a taxi meter running in either direction. Your stake determines how fast the meter ticks, and the market decides which direction it runs in.
Spread betting originated in the UK during the 1970s and remains primarily available in the UK and Ireland. It is regulated as a financial product by the FCA, not the Gambling Commission.
What Is a Spread Betting Account?
A spread betting account differs from traditional share dealing accounts in several important ways. With share dealing, you buy and own shares outright. With spread betting, you never own the underlying asset — you speculate on price direction through a contract with your provider.
Opening an account involves completing an online application, verifying your identity with documents like a passport or driving licence and answering questions about your trading experience and financial situation. Providers must assess whether spread betting is appropriate for you based on your knowledge and experience under FCA rules.
Most providers offer demo accounts where you can practise with virtual funds before risking real money. This proves valuable for beginners who can learn spread betting mechanics without financial consequences.
How Does Spread Betting Work?
Understanding spread betting requires grasping several core concepts that determine your potential profits and losses.
Leverage and Margin Explained
Leverage allows you to control a larger market position with a smaller deposit. If a market has a 10% margin requirement, you deposit £100 to control a £1,000 position. This magnifies both gains and losses proportionally.
FCA rules cap leverage for retail clients at various levels depending on the asset class.
Margin is the deposit required to open and maintain a position. An initial margin opens the trade, while a maintenance margin keeps it open. If your account falls below the maintenance margin, you face a margin call. This is a demand to deposit more funds or close positions to meet the minimum requirement (see below).
Understanding the Stake
Your stake is the amount bet per point of price movement. If you stake £5 per point and the market moves 20 points favourably, you profit £100 (£5 × 20). If it moves 20 points against you, you lose £100.
Choosing your stake size is one of the most important decisions when spread betting. Some risk-management approaches limit exposure per trade, typically 1–2% per trade, though there is no standard method and losses remain common.
What Is the Spread?
The spread is the difference between the buy price (offer) and sell price (bid), representing your cost to enter a trade. For example, if the FTSE 100 quotes 8,200/8,201, the 1-point spread means the market must rise above 8,201 before a long position profits (see below).
What Spread Levels Are Typical?
Spread levels vary by market and provider. Highly liquid markets typically have tighter spreads than less liquid ones. Spreads often widen during volatile periods, outside market hours and around major news events. For example, a spread that is usually 1 point might expand to 5 points during high volatility.
Bet Duration: Cash vs Forward Instruments
Cash bets have no fixed expiry. They roll over daily with overnight funding charges. These suit short-term trades.
In contrast, forward bets have fixed expiry dates, typically quarterly. Funding costs are built into a wider spread rather than charged daily. These may suit investors seeking longer-term positions.
Going Long and Short
Going long means betting prices will rise. You buy at the offer price and profit if markets move up.
Going short means betting prices will fall. You sell at the bid price and profit if markets move down.
This flexibility distinguishes spread betting from traditional investing. In falling markets, you can potentially profit rather than simply watch holdings decline. However, short positions carry additional risks — prices can theoretically rise indefinitely.
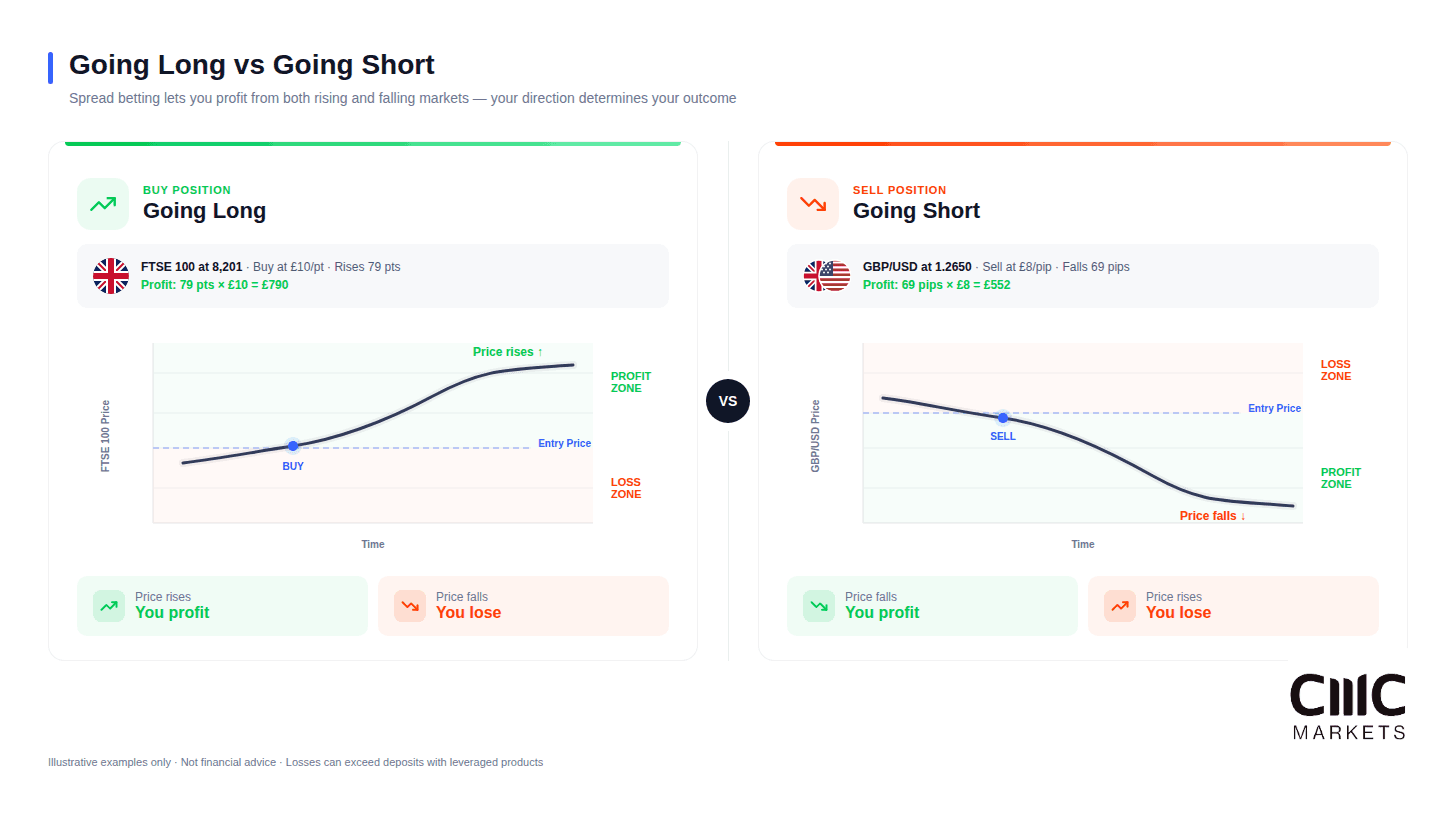
Going long profits from rising prices, going short profits from falling prices.
How to Start Spread Betting in the UK: Five Steps
The steps below are for explanatory purposes only and do not imply spread betting is suitable for you.
Step 1: Open a Spread Betting Account
Choose an FCA-regulated provider and complete your application with personal details and identity verification.
Step 2: Fund Your Account
Deposit funds via bank transfer or debit card. Start with an amount you can afford to lose entirely.
Step 3: Choose Your Market
Select markets based on your knowledge. Beginners often start with major indices like the FTSE 100 or forex pairs like GBP/USD due to high liquidity and tight spreads.
Step 4: Place Your Trade
Decide position direction (long or short), stake size and risk management orders. Before confirming, verify your margin requirement, current spread, stop-loss level and overnight charges.
Step 5: Monitor and Close Your Position
Monitor your position and relevant market factors. Close anytime during market hours by placing an opposite trade.
Spread Betting Examples
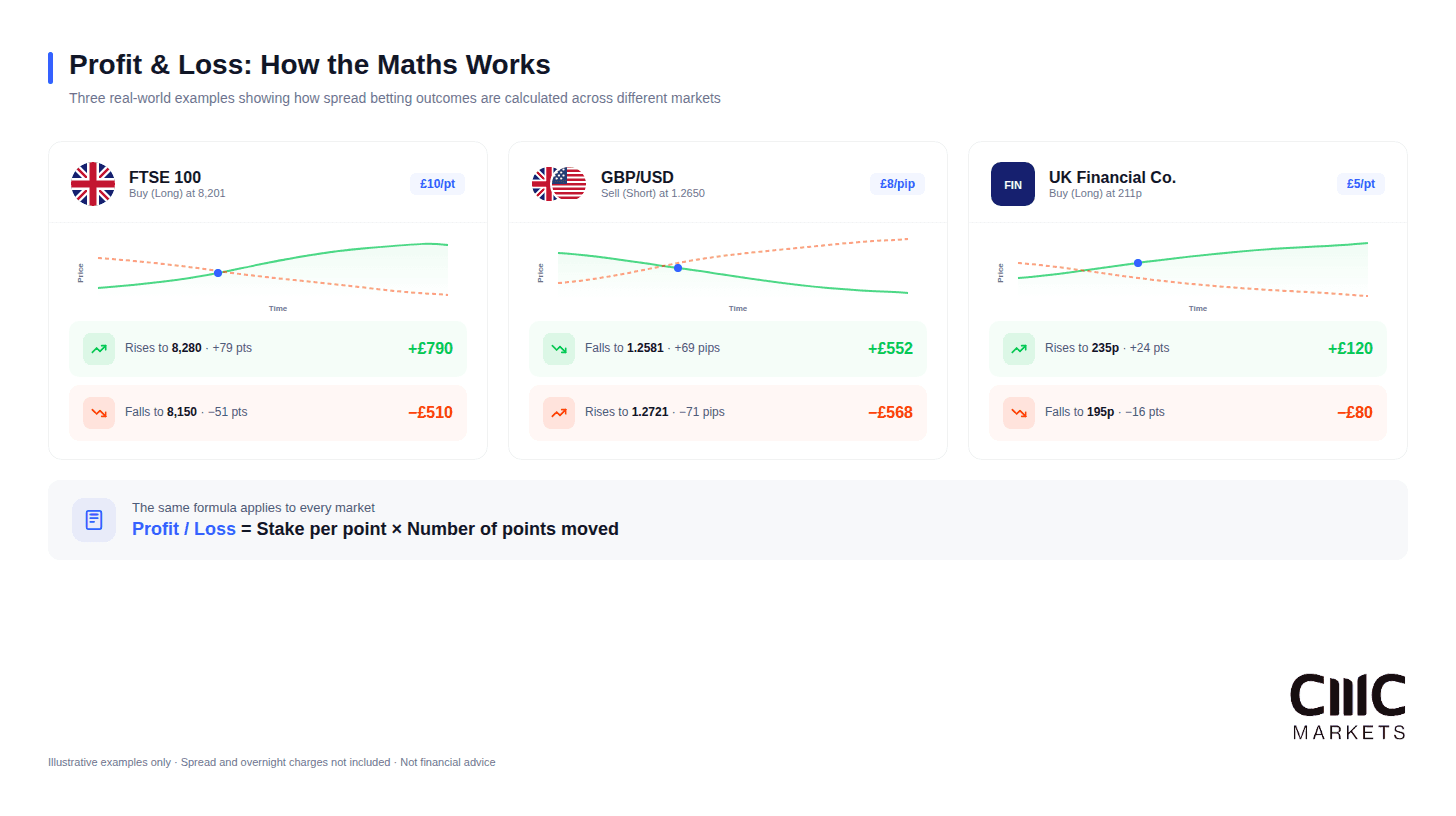
Example 1: Spread Betting on Indices (FTSE 100)
You believe the FTSE 100 will rise. Current quote: 8,200/8,201.
You go long at 8,201, staking £10 per point. With a 5% margin, this requires a deposit of approximately £4,100.50.
Scenario A – Market rises to 8,280: You close at 8,280. Points gained: 79. Profit: £790.
Scenario B – Market falls to 8,150: You close at 8,150. Points lost: 51. Loss: £510.
Example 2: Spread Betting on Forex (GBP/USD)
You expect GBP/USD to decline. Current quote: 1.2650/1.2651.
You go short at 1.2650, staking £8 per pip.
Scenario A – Market falls to 1.2581: Pips gained: 69. Profit: £552.
Scenario B – Market rises to 1.2721: Pips lost: 71. Loss: £568.
Example 3: Spread Betting on Shares
You believe shares in a UK financial company will rise. Current quote: 210p/211p.
You go long at 211p, staking £5 per point.
Scenario A – Shares rise to 235p: Points gained: 24. Profit: £120.
Scenario B – Shares fall to 195p: Points lost: 16. Loss: £80.
Potential Benefits of Spread Betting
Spread betting offers several potential benefits compared to traditional share dealing. However, these come with corresponding risks that must be carefully weighed and will depend on individual circumstances.
Tax-Free Profits in the UK
For most UK residents, spread betting profits are currently exempt from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty. This stems from its classification as gambling under UK tax law.
However, spread betting losses cannot offset other taxable gains. Tax treatment depends on individual circumstances and tax rules may change. If spread betting becomes your primary income, HMRC may treat profits as taxable. Consult a tax professional for further advice.
No Commission on Trades
Most providers charge no separate commission. Costs are built into the spread, simplifying calculations.
Access to Global Markets
You can potentially trade thousands of markets worldwide from a single account: for example, UK and international shares, forex pairs, global indices, commodities and bonds.
The Ability to Trade Rising and Falling Markets
Going short lets you potentially profit when prices fall, which may be valuable during bear markets or for hedging existing portfolios.
Leverage and Capital Efficiency
Leverage provides full market exposure with a fraction of notional value. However, this amplifies losses equally. FCA-mandated negative balance protection prevents retail clients from losing more than their account balance.
Risks and Disadvantages of Spread Betting
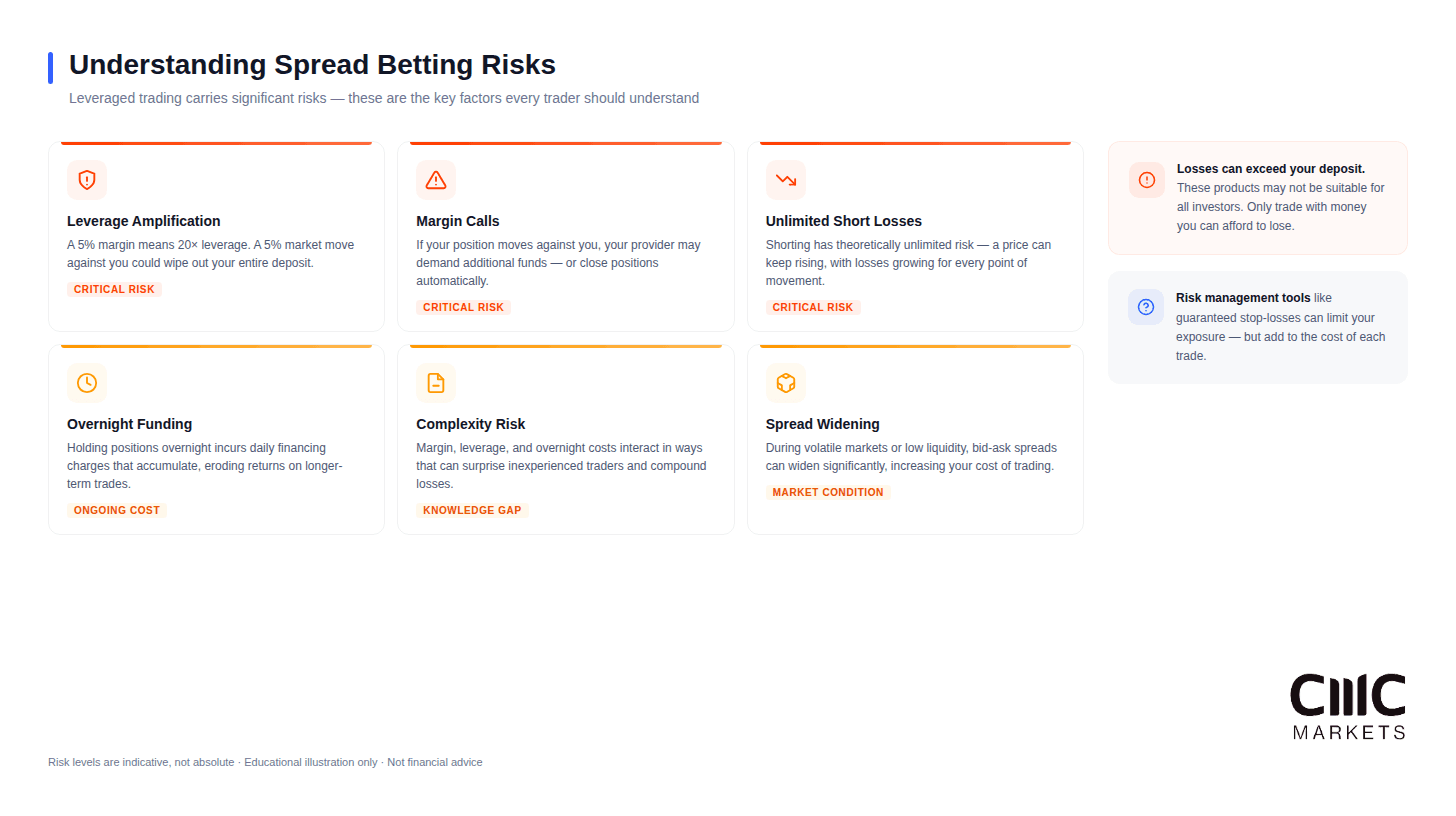
The six key risk factors every spread bettor should understand, from leverage amplification to spread widening.
Understanding material risks is essential before committing capital. These risks explain why most retail traders lose money.
Leverage Amplifies Losses
The same leverage that magnifies gains also equally magnifies losses. A 5% adverse price move on a position with 20:1 leverage wipes out your entire margin. Without adequate risk management, losses can accumulate rapidly.
FCA data consistently shows that approximately 80% of retail spread betting accounts lose money. This statistic reflects the difficulty of consistently predicting short-term price movements while managing leveraged risk effectively.
Risk of Margin Calls and Close-Outs
If your account equity falls below maintenance margin requirements, you will receive a margin call, requiring additional funds or position reduction. If you cannot meet the margin call, your provider may close your positions at current market prices, potentially crystallising significant losses.
Close-outs often occur during volatile markets when prices move quickly. You might be closed out at a much worse price than your stop-loss level during extreme market conditions or gaps.
Complexity for Beginners
Spread betting involves concepts that may be unfamiliar to traditional investors: leverage, margin, funding charges, different order types and reading price quotes. The learning curve can be steep and mistakes made during this phase cost real money.
Wider Spreads During Volatility
Spreads often widen during volatile market conditions, major news events and outside of core trading hours. A market with a normal 1-point spread might quote 5 or more points during high volatility, significantly increasing your trading costs and potentially triggering stop-losses unexpectedly.
Managing Risk in Spread Betting
Effective risk management separates traders who survive from those who deplete their accounts.
Using Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-losses automatically close positions at specified prices, limiting potential loss. Standard stops execute at the next available price after triggering. Guaranteed stops ensure exact execution for an additional premium.
Place stops at logical levels based on market structure, not arbitrary points.
Position Sizing Strategies
Some risk-management approaches limit exposure per trade. For example, risking no more than a small percentage of account equity on any single trade helps reduce the impact of losing streaks, though losses remain common and no approach guarantees success.
Understanding and Avoiding Margin Calls
To avoid margin calls, monitor your margin levels continuously. Avoid overleveraging by keeping position sizes modest. Do not max out your margin on single trades.
Spread Betting vs CFD Trading: Key Differences
Spread betting and trading Contracts for Difference (CFDs) are often mentioned together, as both allow traders to speculate on rising or falling prices in markets without owning the underlying assets.
While spread betting allows traders to ‘bet’ on price movements, CFDs enable traders to speculate on the future value of assets using short-term contracts.
However, there are key differences in the way spread betting and CFD trading are structured, taxed and priced.
*Tax treatment depends on individual circumstances and may change.
The primary UK distinction is taxation. Spread betting profits are typically tax-free while CFD profits face Capital Gains Tax, though CFD losses can offset other gains. Individual circumstances will determine which suits you better. Tax rules may change in future.
Both products carry similar leverage risks.
What Is Forex Spread Betting?
Forex spread betting applies spread betting mechanics specifically to currency pairs. It remains one of the most popular spread betting markets due to high liquidity, tight spreads and extended trading hours.
How Forex Spread Betting Works
Currency pairs are quoted in pips (percentage in point), typically the fourth decimal place for most pairs. For example, GBP/USD at 1.2650 means one pound equals 1.2650 US dollars. A move from 1.2650 to 1.2660 represents a 10-pip change.
Your stake in forex spread betting is quoted as pounds per pip. For example, if you staked £5 per pip and GBP/USD moves 30 pips in your favour, you profit £150.
Major pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD and USD/JPY typically offer the tightest spreads, often less than 1 pip. Minor and exotic pairs have wider spreads reflecting lower liquidity.
The forex market operates 24 hours during weekdays, following trading sessions from Sydney through Tokyo, London and New York. This extended access allows you to react to global economic events and news releases as they occur.
Tax Treatment for Forex Spread Betting
For UK residents, forex spread betting carries the same tax differences as other spread betting: profits are generally exempt from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty. This contrasts with trading forex through a standard broker account, where profits would typically be taxable and must be declared.
This tax treatment makes spread betting a draw for active forex traders who might otherwise face significant Capital Gains Tax bills. However, this will depend on individual circumstances and the inability to offset losses against gains elsewhere remains an important consideration for overall tax planning. Bear in mind that tax rules may also change in future.
Is Spread Betting Tax-Free in the UK?
Current Tax Position
Under current UK law, spread betting is classified as gambling. Gambling winnings are not taxable. For most UK residents, spread betting profits are exempt from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty.
Important Caveats
Losses cannot offset gains. Unlike CFD losses, spread betting losses cannot reduce Capital Gains Tax liability elsewhere.
Some market participants may be taxed. If spread betting becomes your primary income, HMRC may treat profits as taxable income.
Tax rules can change. While spread betting has been tax-free for decades, there is no guarantee this will continue.
Seek professional advice for guidance specific to your circumstances.
Is Spread Betting Gambling?
For tax purposes, spread betting is treated as gambling — the basis for its Capital Gains Tax exemption.
For regulatory purposes, it is treated as a financial product, regulated by the FCA with protections including negative balance protection and leverage limits not available with pure gambling products (see next section).
Functionally, spread betting shares characteristics with both gambling (predicting uncertain outcomes) and investing (analysing markets and fundamentals).
Whether you view spread betting as gambling or trading, material risk remains the same. Most participants will lose money so investors should approach with appropriate caution.
FCA Regulation and Legal Status in the UK
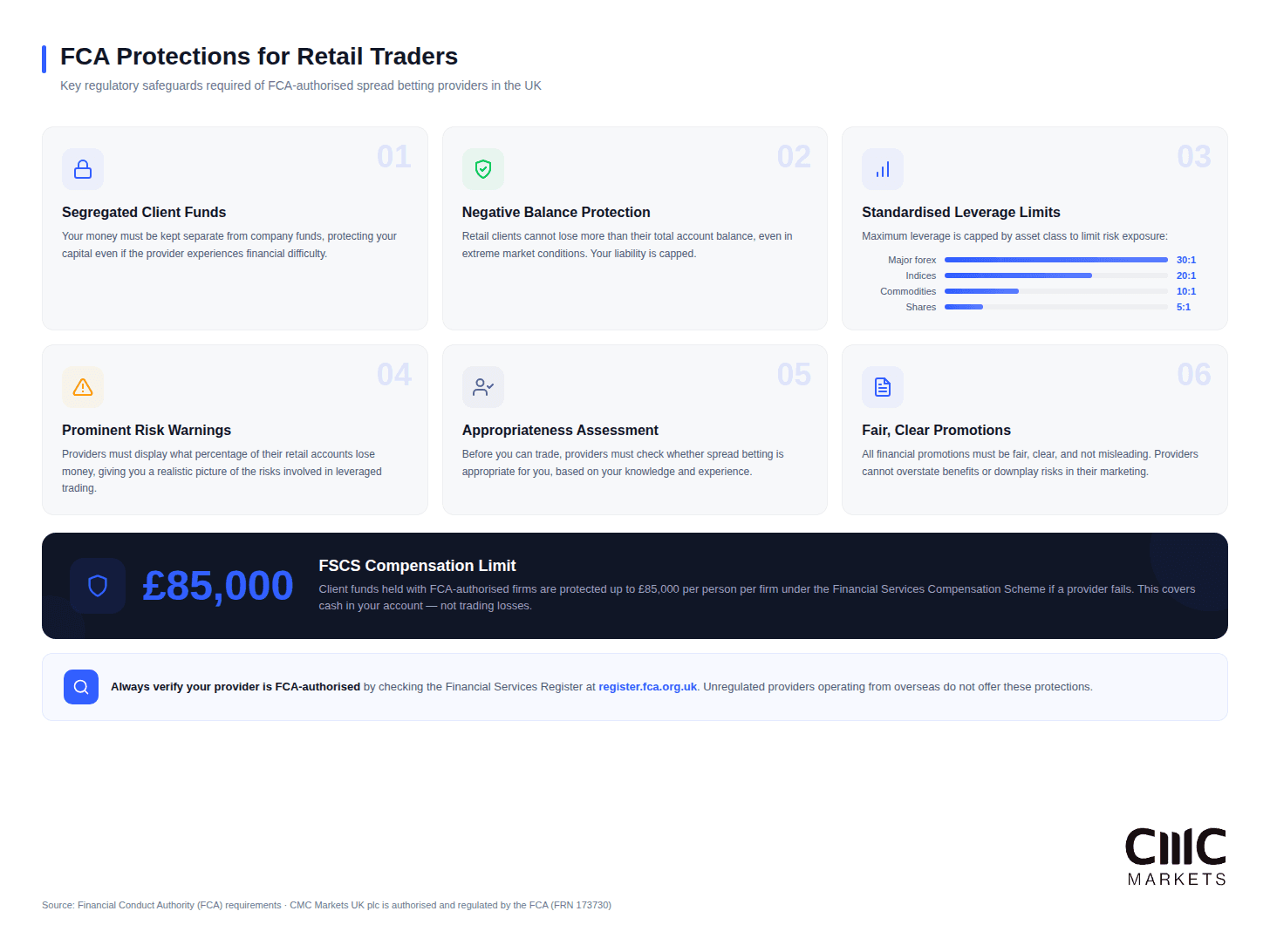
Spread betting in the UK operates under the FCA’s oversight, which provides important protections for retail traders.
The FCA requires spread betting providers to:
Segregate client funds from company funds to protect client money
Provide negative balance protection, ensuring retail clients cannot lose more than their account balance
Apply standardised leverage limits based on asset class risk profiles
Display prominent risk warnings, including the percentage of retail accounts that lose money
Assess product appropriateness based on client knowledge and experience
Ensure financial promotions are fair, clear and not misleading
Client funds held with FCA-authorised firms are protected up to £85,000 under the Financial Services Compensation Scheme (FSCS) if a provider fails. This protection covers cash held in your account, not market losses from trading.
Always verify your provider is FCA-authorised by checking the FCA’s Financial Services Register at register.fca.org.uk. Unregulated providers operating from overseas do not offer these protections and should be avoided.
Spread betting is a leveraged derivative allowing speculation on financial market price movements without owning underlying assets. You stake an amount per point and make a profit or loss based on market direction. Profits are currently exempt from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty for most UK residents, though losses cannot offset other gains and tax rules may change in future. Whether spread betting is appropriate for you will depend on individual circumstances
For most UK residents, profits are currently free from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty. However, losses cannot offset gains, tax depends on individual circumstances and HMRC may tax profits if spread betting becomes your primary income. Consult a tax professional for advice.
It’s legally classified as gambling for UK tax purposes, but regulated as a financial product by the FCA, not the Gambling Commission. FCA regulation provides protections like negative balance protection that are not available with pure gambling products.
Spread betting profits are typically tax-free while CFD profits face Capital Gains Tax (though, as mentioned, losses offset gains). Spread bets use stake per point in GBP; CFDs use contracts in the underlying currency. Both carry similar leverage risks.
Retail clients with FCA-regulated providers have negative balance protection — meaning you cannot lose more than your account balance. However, you can still lose your entire deposit.
While many providers have no minimum, some traders choose to start with modest amounts to allow position sizing flexibility. The appropriate amount will vary by individual circumstances.
This occurs when account equity falls below maintenance margin requirements, and requires additional funds or position reduction as a result. Unmet margin calls result in automatic position closure.
Thousands of markets including UK and international shares, major and minor forex pairs, global indices, commodities and bonds. Available markets will vary by provider.
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). Authorised providers must segregate client funds, offer negative balance protection, apply leverage limits and display risk warnings.
Major forex pairs typically have spreads of 0.6–1 pip. FTSE 100 typically quotes 1–2 points. Gold spreads are typically 0.3–0.5 points. UK shares often have spreads around 0.1% of the share price. Spreads widen during volatility, major news and outside core trading hours.
Cash or rolling spread bets incur overnight funding charges when held past market close. These are calculated as position value multiplied by the benchmark rate plus or minus provider markup, divided by 365. For long positions, you typically pay funding. For short positions, you may receive funding if benchmark rates are positive, though provider markups often mean you still pay a small charge.
Spread betting is a complex, high-risk product where most retail participants lose money. Beginners face a steep learning curve covering leverage, margin and market analysis. If you are new to trading, it is prudent to start with a demo account, where you can educate yourself thoroughly, and begin with small stakes if you progress to live trading. Consider whether spread betting aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance before committing capital.
2 Except in some circumstances which may be outside of our control.
Any questions?
Email us atWe're available whenever the markets are open, from Sunday night through to Friday night.