What is forex trading?
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading or FX trading, involves converting one currency into another – for example, British pounds into US dollars. Forex trading takes place over the foreign exchange market – a global, decentralised market made up of computer networks and trading terminals. It is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, with daily trading volume reaching $7.5 trillion. Forex traders buy and sell currencies with the aim of making a profit on changes in exchange rates.
What is forex trading and how does it work?
Foreign exchange trading is also known as FX trading or forex trading provides the opportunity to speculate on price fluctuations within the FX market. FX is an industry term that is abbreviated from forex and is commonly used instead of forex. However, forex is also an abbreviation of foreign exchange.
The goal of FX trading is to forecast if one currency’s value will strengthen or weaken relative to another currency. A forex trader will encounter several trading opportunities each day, due to daily news releases. They take advantage of this by becoming extremely receptive to market news releases and then trade based upon the suspected market sentiment.
What are forex currency pairs
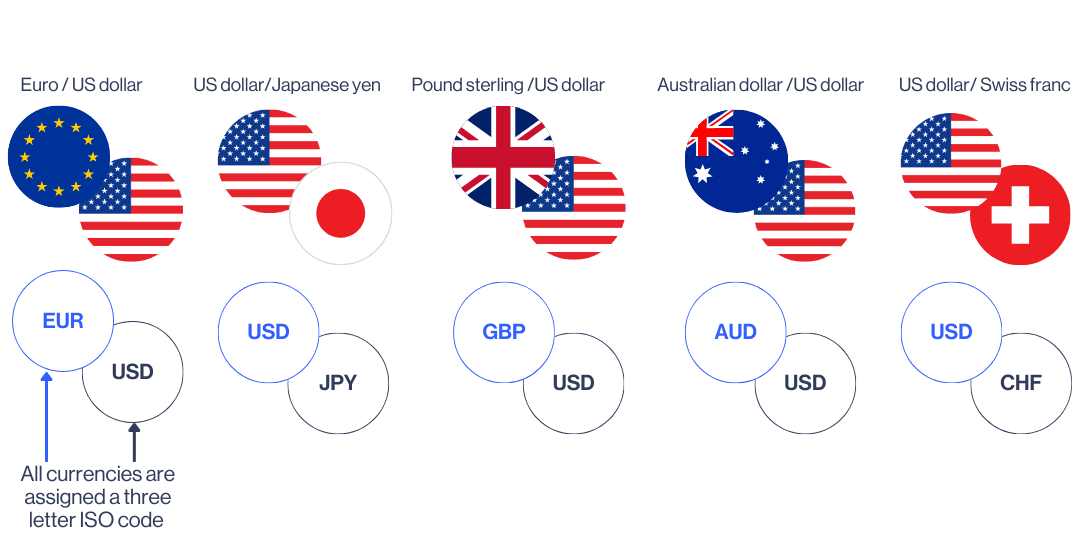
A forex pair is a combination of two currencies that are traded against each other, such as the British pound (GBP) and the US dollar (USD). Forex trading works by speculating against the difference in valuation of two currencies.

The base currency is always on the left of a currency pair, and the quote or counter currency is always on the right. The base currency is equal to one, and the counter currency is equal to the current quote price for the pair.
In the above example, GBP is the base currency and USD is the counter currency. If the current quote for GBP/USD is 1.2500, that means £1 is trading at $1.25.
What are the different types of forex pair?
Forex pairs are often categorised into three different groups: majors, minors (or crosses) and exotics:
Majors combine the US dollar with the world's other heavily traded currencies. These are the most liquid pairs on the forex market.
💡 Examples:
GBP/USD (British pound / US dollar)
EUR/USD (euro / US dollar)
USD/JPY (US dollar / Japanese yen)
Minors, also known as crosses, do not include the US dollar, but involve other major currencies.
💡 Examples:
EUR/GBP (euro / British pound)
AUD/NZD (Australian dollar / New Zealand dollar)
GBP/JPY (British pound / Japanese yen)
Exotics consist of one major currency and one from a small or emerging market. These pairs often have higher spreads and lower liquidity, making them more volatile.
💡 Examples:
GBP/ZAR (British pound / South African rand)
USD/TRY (US dollar / Turkish lira)
EUR/SEK (euro / Swedish krona)
What is a pip?
A pip (short for 'percentage in point') is the smallest standardised unit of measurement by which a forex quote can change. For GBP/USD, a pip is a movement of 0.0001. So, for example, if GBP/USD moves from 1.2400 to 1.2401, that’s a one-pip price movement.

Most currency pairs, including GBP/USD, EUR/USD and AUD/USD, are quoted to five decimal places. One pip is represented by the fourth decimal place (0.0001). The fifth decimal is not a pip, but is known as a baby pip or 'pipette'. On our trading platform, the baby pip appears as a smaller digit than the other numbers that make up the quote.
For forex pairs that involve the Japanese yen, such as USD/JPY, a pip is the second decimal place (0.01), not the fourth. So, a one-pip change for USD/JPY would look like this: 145.00 → 145.01. With USD/JPY, the third decimal is the baby pip.
What is a lot?
A lot in forex refers to the size of a trade. Since forex is traded in large volumes, lots help to standardise how much of a currency you buy or sell in one trade. A standard lot represents 100,000 units of the base currency (the currency on the left of the pair). So, for GBP/USD, a standard lot would represent £100,000.
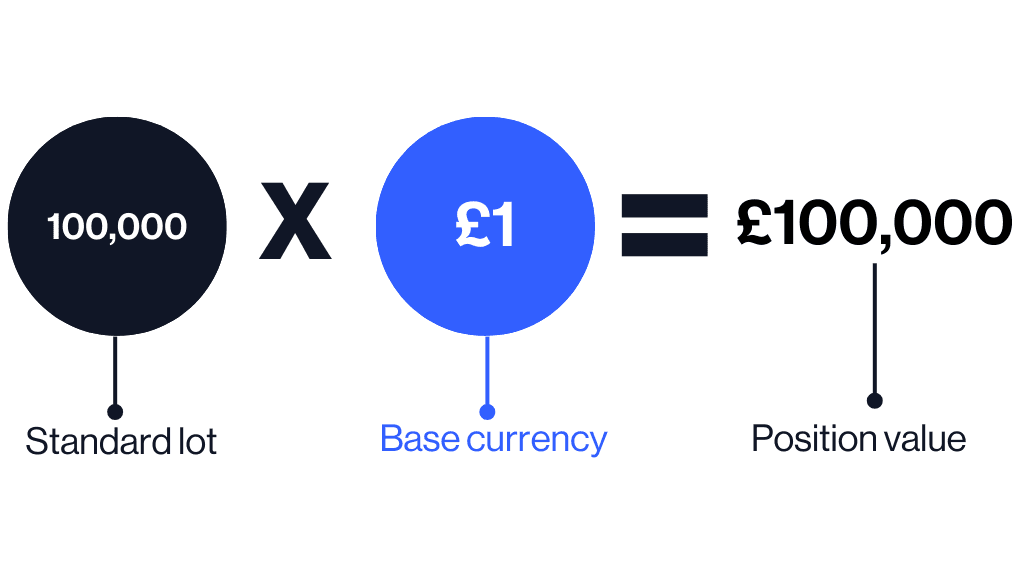
There are three main lot sizes:
Effect of lots on forex trades
Understanding lot sizes is an important part of risk management. If you increase your lot size, you're taking on more risk. The larger the lot size, the greater the potential profit or loss.
If you trade a standard lot, a one-pip move equates to £10 gained or lost.
If you trade a mini lot, a one-pip move represents £1 profit or loss.
If you trade a micro lot, a one-pip move equals a 10p profit or loss.
How to trade the FX market
Trading a currency pair means you expect the base currency to strengthen relative to the counter currency, while selling a currency pair means you expect the base currency to weaken. For example, buying GBP/USD means you believe the pound will strengthen against the dollar, and selling GBP/USD means you think the pound will weaken.
In the past, you might have traded forex over the phone via a forex broker. Nowadays you can trade forex online with a spread betting or contract for difference (CFD) trading account, both of which are available from CMC Markets.
Spread betting and CFD trading are forms of derivative trading. This means you don't own the underlying asset, but instead speculate on its price movements. Spread betting and CFD trading also provide the opportunity to trade forex with leverage, a subject we explore in the next section.
Trading forex through a broker
Once you've done your research, formulated a trading strategy and developed a trading plan you can stick to, you might be ready to open a trading account with a broker, such as CMC Markets.
With us, you can open a demo account to practise trading forex risk-free with virtual funds. When you're ready to trade for real, you can step up to a live account. Before you start trading live markets, it's a good idea to learn how to use our risk-management tools, such as stop-loss and take-profit orders. These features can help to protect your downside and lock in any gains you might make.
What is leverage in forex trading?
Leverage enables you to enlarge your financial position and increase the potential return of a trade. When you open a leveraged trade, you deposit a fraction of the full value of the trade (known as the 'margin') while your broker lends you the rest. It's important to remember that leverage amplifies potential profits and losses equally, making it riskier than traditional investing.
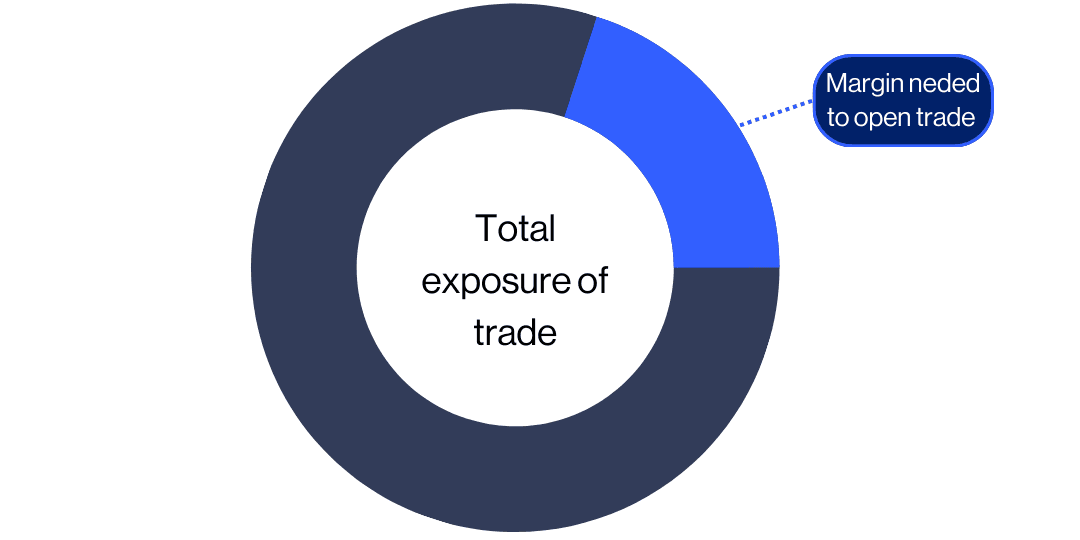
Our competitive margin rates on forex pairs start from just 3.3%, or 30:1 leverage. The amount of leverage available on forex trading tends to be greater than for asset classes such as shares (5:1).
What is the spread in forex trading?
In forex trading, the spread is the difference between the buy and sell price of a currency pair. When you trade forex pairs, you are offered a ‘buy’ price that is often above the market price and a ‘sell’ price that is often below the market price. The difference between these two prices is referred to as the ‘bid-ask’, or ‘buy-sell’, spread.
Forex trading has some of the lowest spreads of all financial instruments. Our forex spreads start from just 0.5 pips (or 0.0 with our FX Active account), compared to a minimum spread of 1 point for many indices, or 2.5 points for crude oil. Learn more about our forex spreads and margins here.
Forex trade example
Let's imagine that you've looked at the news nd spotted a development that you think could mean the pound strengthens against the US dollar. You decide to go long on, or 'buy', GBP/USD at 1.2500 with a position size of 10,000 units (one mini lot).
Successful outcome
Next, let’s assume your hunch proved correct and GBP/USD rises to 1.2600, a 100-pip increase (1.2600 - 1.2500 = 100 pips) from your trade entry point. You close your trade at 1.2600, locking in a profit of £100.
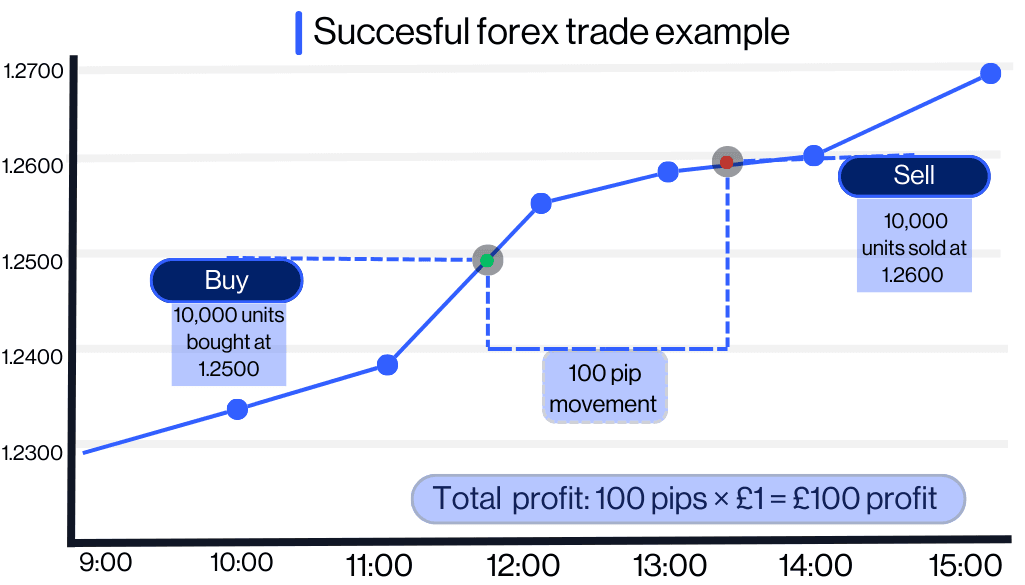
Pip value for one mini lot (10,000 units) = £1 per pip
Total profit: 100 pips × £1 = £100
Your £334 margin deposit remains intact, and you made a profit of £100, giving you a new balance of £444
Unsuccessful outcome
Now let's assume you were wrong and GBP/USD falls to 1.2400, a 100-pip decrease (1.2500 - 1.2400 = 100 pips). You close your trade at 1.2400, incurring a loss of £100.
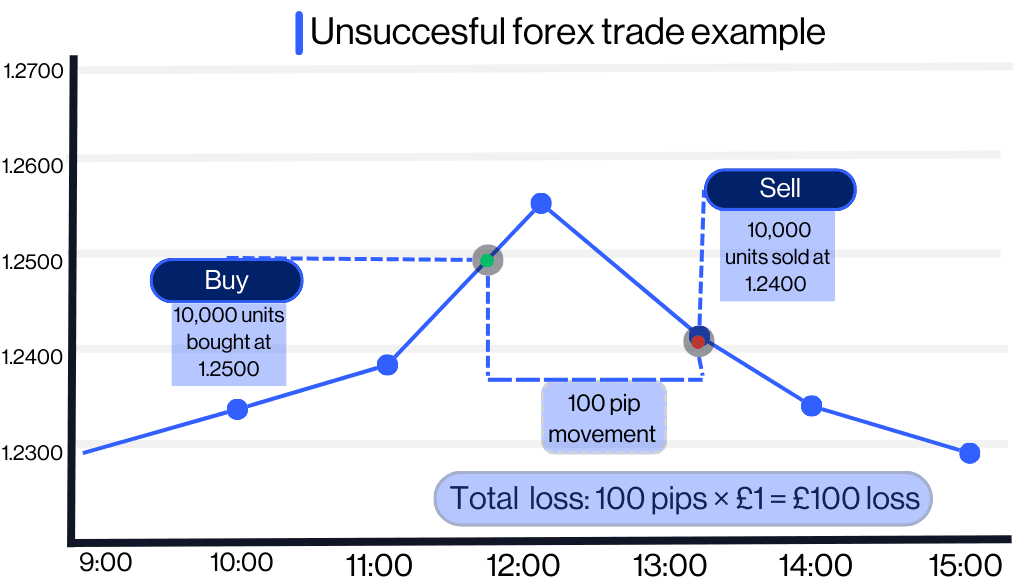
Pip value for one mini lot (10,000 units) = £1 per pip
Total loss: 100 pips × £1 = £100 loss
After £100 is deducted from your £334 deposit, your new balance is £224
🚨 Remember: Leverage amplifies your profits and losses equally. Your position size also increases your risk exposure. As the above example shows, a 100-pip move resulted in a £100 gain/loss when trading a mini lot of 10,000 units, but a larger position size (such as a standard lot of 100,000 units) would have resulted in a loss of £1,000 on the same initial outlay.
Where is the forex market and when is it open?
The forex market has no central marketplace or trading floor, but instead operates across a huge network of interconnected computers and trading terminals. It is open 24 hours a day from Sunday night through to Friday night. Read more about forex market hours.
The importance of research
How would you get a sense that the pound might strengthen versus the dollar? For that you'd need to carry out your own research, conduct technical and/or fundamental analysis, and keep up to date with financial news, market events and any unexpected announcements that could affect sentiment.
Forex trading as insurance policy
Forex trading is used not only for speculation but also for hedging. Forex hedging is when businesses and individuals use forex trading to protect themselves from unfavourable currency movements. For example, a company doing business overseas might use forex trading to insure against potential losses caused by fluctuations in the exchange rate.
Who trades forex?
Most forex trading is done by central banks, retail and investment banks, and multinational corporations, but retail traders also play an important role. Understanding how each of these players interact with the forex market can help traders to understand market trends and price fluctuations.
Central banks are responsible for managing their nation’s currency, money supply and interest rates. They sometimes intervene in currency markets to stabilise their nation’s currency.
Banks trade large volumes of currency on the interbank market. Banks exchange currencies with other banks, either on behalf of their own accounts or on behalf of large organisations.
Corporations trade forex to manage currency risk, facilitate international transactions and pay for imports, exports or other services.
Retail traders account for a smaller proportion of forex trading than banks and corporations. Individual traders speculate on the forex market in a bid to profit from currency fluctuations.
What factors influence the forex market?

Forex rates are influenced by a complex interplay of political, economic and market forces, including:
Elections
Political stability (or the lack of it)
Inflation
Interest rates,
Trade balances,
Government borrowing
Market sentiment
Below, we look at some of these factors in more detail.
Politics
Politically stable nations generally have stronger currencies as investors tend to be more confident in these countries' long-term economic prospects. In contrast, countries that experience political instability – perhaps in the form of coups, civil unrest or large-scale corruption – often have weaker currencies because instability erodes investor confidence. This can lead to 'capital flight' as investors move their money to safer countries. The outflow of capital reduces demand for the country's currency, causing it to depreciate in value.
Interest rates
Central banks control a country's or economic bloc's benchmark interest rate, raising rates to curb spending and tame inflation, or cutting rates to encourage spending and stimulate economic growth. At the same time, higher interest rates make deposits in that currency more attractive to investors, increasing both the demand for and the value of that currency. In this way, higher interest rates attract foreign investment. Meanwhile, lower interest rates can have the opposite effect, reducing demand for the currency and deterring foreign investment.
Inflation
High inflation rates generally lead to a weaker currency as sharp increases in the price of goods reduce the purchasing power of the currency. Conversely, low inflation means stable prices, which boosts investor confidence in and demand for the currency, helping to strengthen its value, especially when paired with high interest rates.
Terms of trade
Terms of trade, a measure which compares a country's export prices to its import prices, affect forex rates by influencing demand for a country's currency. For example, if a country’s export prices rise relative to its import prices (an improvement in terms of trade), demand for its currency increases as foreign buyers are willing to pay more for its goods. This increase in demand can cause the currency’s value to rise. If a country's currency appreciates, its exchange rate versus other currencies may increase, making its goods and services more expensive for foreign buyers, and making its imports cheaper.
Government debt
High levels of public debt can lead to concerns about a country's ability to repay its debts, potentially weakening its currency. The loss of investor confidence in a country's economy can result in capital flight and a decrease in demand for the country's currency, leading to a depreciation in the currency's value relative to other currencies.
What are the benefits of forex trading?
Leverage: Trading forex with us allows you to trade with leverage, also known as trading on margin. Remember, leverage amplifies profits and losses.
High liquidity: As the forex market is the largest financial market in the world, it has high levels of liquidity, making it easy to enter and exit positions quickly, at least on majors such as EUR/USD.
Availability: Traders can access the forex market 24 hours a day, five days a week.
Go long or short: When spread betting or trading CFDs on forex, you can go long or short on a currency pair, depending on whether you think the rate will rise or fall.
Variety: The forex market offers a wide range of choice – with us you can trade on more than 330 forex pairs.
What are the risks of forex trading?
Amplified losses: You could lose all of your capital when trading forex with leverage. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also magnifies potential losses, since your profit or loss is based on the full value of the position.
Market volatility: The forex market can be volatile, meaning that currency prices may fluctuate rapidly and unpredictably, potentially leading to losses.
Account close-out: Market volatility and rapid price swings can cause the balance of your account to fluctuate. If you do not have sufficient funds in your account to cover losing positions, your broker may automatically close your trades.
Economic announcements: Interest rate rises/cuts, trade tariffs, and other economic policy decisions can influence currency values, potentially impacting your forex trades.
Unexpected events: Political instability, economic crises and other unforeseen developments can cause currency fluctuations and potential losses.
Inexperience: Some traders, particularly those new to trading, may chase losses, trade on emotion, or simply trade too much, resulting in poor trading decisions and potential losses.
Bottom line
As the largest financial market in the world, the forex market is a complex, fast-moving and dynamic world, with trillions of dollars at stake every day. Banks, corporations and individuals participate in forex trading to speculate on rising and falling prices, and to hedge against risks in other areas of their business or portfolio. From pips to lots and spreads, there is a lot of specialist terminology that new forex traders need to learn and understand before they trade live markets. Currencies are influenced by various factors, many of which are outside traders' control, such as inflation and interest rates.
Leveraged forex trading brings potential rewards and risks. By increasing your market exposure, leverage amplifies potential profits and losses equally. Skilled and experienced forex traders often specialise in trading a few select currency pairs, investing their time in understanding the economic and political factors that move those currencies.
To learn more about forex trading, check out our step-by-step guide on how to start forex trading.
There are plenty of online resources out there that can help you learn to trade forex. Discover the basics at our learn forex page, which covers a wide range of topics, including margin and leverage, pips, forex market hours and forex trading strategies.
To get to grips with forex on our trading platform, you can open a forex demo account to practise trading with £10,000 of virtual funds.The seven most traded currency pairs in the world are EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, AUD/USD, USD/CAD, USD/CHF and NZD/USD. Together these seven currency pairs accounted for about 70% of global forex trading in 2022, according to the Bank for International Settlements.
You can’t trade forex without using leverage on our platform. If you’re concerned about the risks of leverage, there are a number of risk-management tools, such as stop-losses and take-profit orders, that could be used when placing a trade. Learn about the execution and order types available on our platform.
There isn't necessarily such a thing as the 'best' forex strategy, because what suits one trader might not work for another. Finding a forex trading strategy that works for you depends on a range of factors, including your risk appetite. There are many different types of strategies, including day trading, swing trading, and scalping. Learn more about trading strategies.

16 strongest currencies
Explore the 16 most powerful currencies in the forex market and the factors that drive their performance. Understand how GDP, trade volume, and monetary policies shape their movements and global influence.
Disclaimer: CMC Markets is an execution-only service provider. The material (whether or not it states any opinions) is for general information purposes only, and does not take into account your personal circumstances or objectives. Nothing in this material is (or should be considered to be) financial, investment or other advice on which reliance should be placed. No opinion given in the material constitutes a recommendation by CMC Markets or the author that any particular investment, security, transaction or investment strategy is suitable for any specific person. The material has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research. Although we are not specifically prevented from dealing before providing this material, we do not seek to take advantage of the material prior to its dissemination.