Spread betting vs CFD trading
Understand the key differences between spread betting and contracts for difference (CFDs); both are margined products and forms of financial derivative trading. They both provide similar benefits yet boast their own advantages and carry their own risks.
Main differences between CFDs and spread betting
Taxation- A key difference between spread betting and CFD trading is the taxation of profits. Gains from spread betting are tax-free¹, while profits made from CFD trading are subject to capital gains tax. As neither product results in ownership of the asset traded, there’s no stamp duty charge.
Regional availability- Another difference is regional availability – spread betting is only available in the UK and Ireland, whereas CFD trading is available in many countries globally.
Currency considerations- Profits and losses from spread betting are realised in the currency you bet in. For CFDs, profit and loss is realised in the traded market’s base currency, and therefore is subject to a currency risk. Both trading methods allow for going long or short, although there are some differences in terms of pricing.
CFD and spread betting trade example
Trading on the UK 100
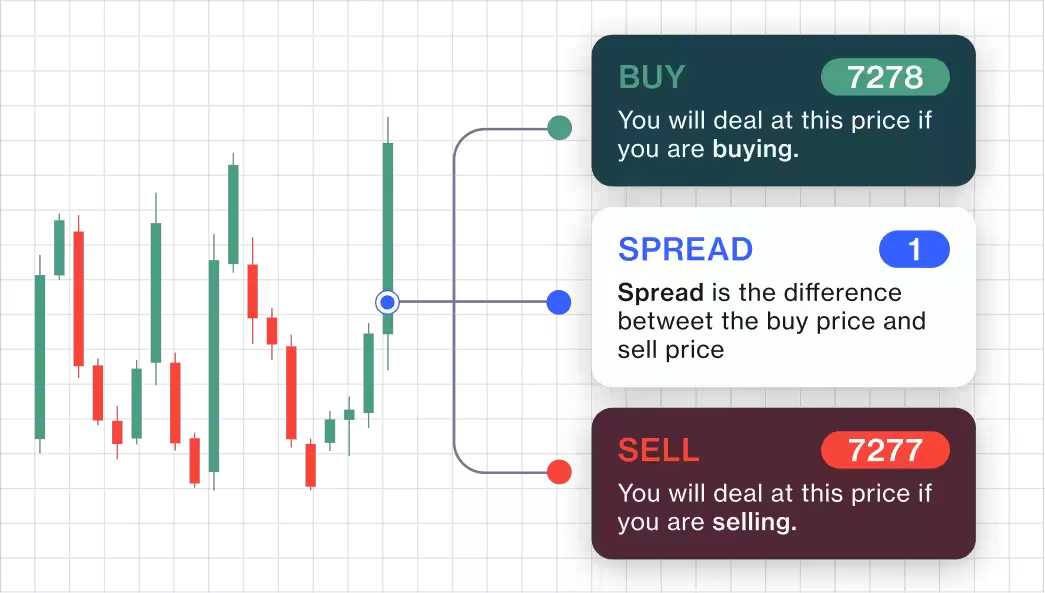
Here’s an example of how to trade on our UK 100 – Cash instrument, which is based on the UK’s benchmark stock index measuring the performance of 100 companies. The following information is the same for both spread bet and CFD products:
Sell price = 7277
Buy price = 7278
Spread = 1
Margin rate = 5%
Let’s assume you think the price of the UK 100 will rise, so you open a buy (long) position with the hoping to profit from a rise in the index's value
The UK 100 has a margin rate of 5%, which means you only need to deposit 5% of the total value of the trade as your position margin.
The UK 100 then moves to a new sell price of 7302 and buy price of 7303. This means your prediction is correct and the instrument rose in value. You decide to close your bet by selling at the new sell price of 7302.
What about any extra charges?
View our spread betting and CFD trading costs.
Spread betting or CFD trading: which is right for me?
CFDs vs spreads betting: in-depth comparison
Under the FCA's Client Money rules, we're required to segregate client money (unless you agree with us otherwise) from CMC's own funds. The funds held in segregated bank accounts do not belong to CMC, and will be held in a way that enables it to be identified as client money. Learn more about client money regulations
Yes, we do offer affiliate and introducer incentives. The program is designed to remunerate and reward introducers and partners who refer clients to CMC Markets. As an affiliate, you can earn a commission for referring new clients to CMC Markets. The commission rate varies depending on the country where your referrals are based. As an introducer, you will earn a commission on the trading activity of your clients. CMC Markets offers flexible and competitive rebate structures, including multi-tiered rebate structures to maximise your earning potential.
Apply here to join the CMC Markets introducer program
On our desktop trading platform and mobile apps, select the buy or sell price for your chosen instrument, and an order ticket will appear. Choose between a ‘Market Order’, ‘Limit Order’, or ‘Stop Entry Order’, enter your trade size and any ‘Stop Loss’ or ‘Take Profit’ levels, then place your trade by selecting the ‘Place Buy Market Order’ or ‘Place Sell Market Order’ button.